3rd Series of International Workshop on
(3SCity-E2C) Building Software Services in Smart City through
Edge-to-Cloud orchestration
Special ICT Themes:
- Resource Management for Software Service Execution
Special Business Domains Themes:
- Digital Twins for smart building, EMS, and neighborhoods
+ Our particular interest focuses on “Reducing end-use Energy Demand” in building and neighborhoods
- Connected Cars and Vehicular Network Solutions
in conjunction with The 22nd IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Toronto, Canada
June 15-18, 2021
Download Call For Paper (CFP-3SCity-E2C 2021 Workshop)
Note that for each content you used on this page, please cite the below information in your reference list.
+Reference template: Sinaeepourfard, Amir; Sengupta, Souvik, “3SCity-E2C: Building Software Services in Smart City through Edge-to-Cloud orchestration,” 3rd Int’l. Wksp. Building Software Services in Smart City through Edge-to-Cloud orchestration, 2021; https://fmezen.no/3scity-e2c-workshop-2021-3rd-edition/.
++ Reference template for Figures: If “Figure” has a particular reference in our text, please put the direct reference of Figure in your text.
About IEEE MDM 2021 Conference:
The MDM, International Conference on Mobile Data Management, series of conferences, since its debut in 1999, has established itself as a prestigious forum for the exchange of innovative and significant research results in mobile data management. The conference provides unique opportunities to bring researchers, engineers, and practitioners together to explore new ideas, techniques, and tools and exchange experiences. The conference this year is hosted by the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science department of York University.
Comprising both research and industry tracks serves as an important bridge between academic researchers and industry researchers. Along with the presentations of research publications, it also serves as a meeting place for technical demonstrations (demos), workshops, advanced seminars, panel discussions, as well as Ph.D. forums and Industrial forums to cater to Ph.D. students and industrial developers.
The conference focuses on research contributions in data management in mobile, ubiquitous, and pervasive computing.
More information is available at this link.
About the Third Series of the International Workshop on 3SCity-E2C:
We organized the “3Scity-E2C” international workshop from 2020. The first and second series of the international “3SCity-E2C” workshops were organized successfully, as shown details below:
- The first edition of IEEE 3SCity-E2C was organized in conjunction with IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (IEEE MDM 2020). The first series of the 3SCity-E2C workshop focuses on the design, implementation, and operation of integral solutions for “Large-Scale Data Management to build Software Services in Smart Cities through Edge-to-Cloud orchestration.”.
- The second edition of ACM 3SCity-E2C was organized in conjunction with ACM International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking (ICDCN 2021). The second series of the 3SCity-E2C workshop focuses on Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) challenges in smart cities, mainly concentrate on distributed-to-centralized ML and AI techniques (D2C-ML&AI).
This workshop provides a forum to discuss the theoretical foundations and original technical contributions of developing software services and their related “resource management mechanism for software service execution in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities.” This workshop will also highlight how intelligent resource management mechanisms can create through “Predictive and Learning Approaches based on distributed-to-centralized (D2C-ML&AI)” in multilevel ICT architecture of large-scale IoT networks of smart cities. We are interested in novel proposals based on Edge-to-Cloud computing solutions by bringing together industry, academia, engineers, and researchers. Proposals can contribute to all different domains of the Smart Cities (such as transportation, healthcare, energy, and grid) as well as different data analysis scopes (such as cybersecurity challenges and solutions for threat and attack detection, and resource allocation and consumption). However, our special ICT theme for this year is “intelligent resource management mechanism orchestration.” Also, our special business domain themes are i) “digital Twins for smart building, energy management system (EMS), and neighborhoods,” and our particular interest focuses on “reducing end-use energy demand in building and neighborhoods;” ii) “connected cars and vehicular network solutions.”
All accepted papers will be published in the proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Mobile Data Management and included in the IEEE Xplore® digital library.
In the series of “3SCity-E2C” workshops, we would like to highlight the importance of “smart cities” concepts through the Sustainable Development Goals, in particular, “Goal 11: Make cities inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable.” Also, we would like to send our special thanks and greetings to the first women who accepted to be part of our committee members in our workshop. We are honor to use her expertise to assist us in this series of workshop activities and organization. Thanks for all Shehnaz Shaik, Ph.D.. We always have full-respect for “gender equality” and “diversity” in our scientific workshop’s organizing procedures.

Reference of Figure and photo-credit: Extracted from https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/
The challenge
-
The main idea of 3SCity-E2C Workshop:
The main idea of “building software services in smart city through edge-to-cloud orchestration” was proposed in the first series of the 3SCity-E2C workshop. This workshop series focuses on how the “resource management mechanism” through multilevel information communication technology (ICT) architecture can be beneficial for the effective and intelligent software service execution in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities.
- The main idea of the “3rd 3SCity-E2C Workshop:”
This series of our workshops aim to integrate all idea of the past “3SCity-E2C” workshop, including “3SCity-E2C,” “D2C-ML&AI,” “Special Track of D2C-ML&AI.” So, we propose the idea of how we can build the “intelligent resource management mechanism for Service Execution of large-scale IoT Networks.” This highlights the collaboration of “Software Engineering Development,” “ML/AI applied to IoT,” “facilities of multilevel ICT architectures,” and “edge-to-cloud computing orchestration.”
1. Research Questions and Problem Statement:
Cloud services and solutions are hot resolutions for small businesses to global enterprises. However, they remain a broad concept covering much online territory. As you start to shift your business to cloud solutions, whether, for application or infrastructure deployment, it is more critical than ever to know the differences and benefits of multiple cloud services. Though “as-a-service” types are increasing by the day, there are regularly three models of cloud service to compare, including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), as shown in Fig 1.
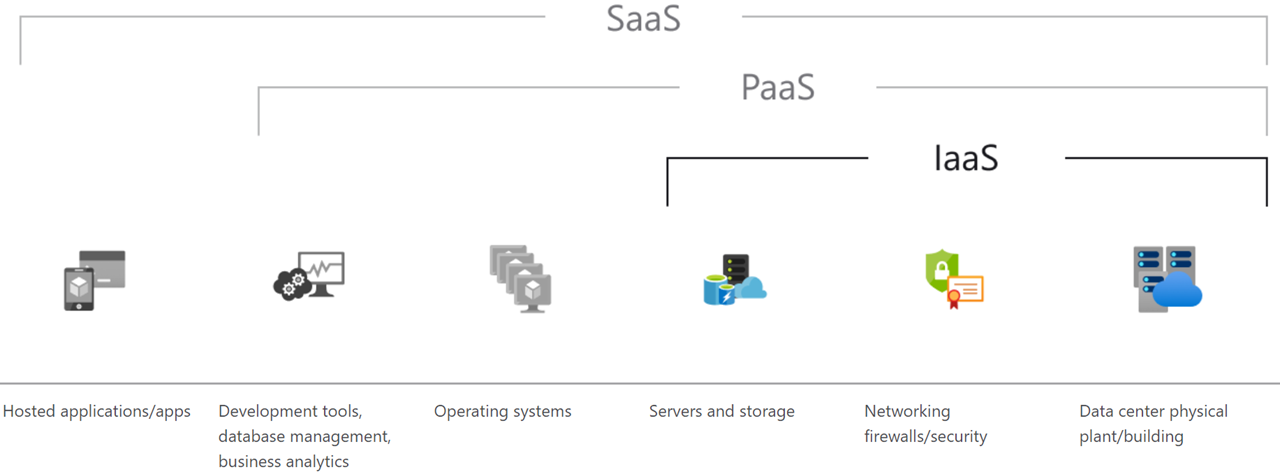
Figure 1. SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS [1]
Recently, several questions have come up about how we can adopt three models of cloud service to edge computing. Some works for each of those are available to present how it could be done at Fog/Edge layers, but there are still several doubts and questions. So, one question is an adaptation to edge layers. Another question is how we can build an intelligent orchestration from edge-to-cloud that makes it possible to connect all three models of cloud service solutions to edge solutions. We called it “E2CaaS: Edge-to-Cloud-as-a-Service” and their related solutions to all three cloud service models.
2. Objectives:
As shown in Fig 2., multilevel ICT architectures are designed based on different ICT and business domain requirements. Recently, there are several efforts to integrate “software service development,” “applied advanced machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to IoT,” and “ICT management requirements” in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities.
In this series of workshops, we are interested in discussing and designing integral ICT architecture solutions for “software service development” through “advanced ML and AI” for smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks. So, the main discussion points and targets are shown below:
- We go beyond different “advance ML and AI techniques” that may be applied to large-scale ICT management of smart cities, such as “AI at Fog/Edge,” “AI at Cloud,” or any other integral AI solutions for large-scale IoT networks of smart cities which are yet demanding and we are looking for further scientific discussion.
- We present different software service development solutions in smart cities, such as “Edge-as-a-Service,” “MEC-as-a-Service,” “Fog-as-a-Service, “cloudlet-as-a-Service, etc. We have recently proposed our integral architectural solution to develop software services in smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks based on edge-to-cloud orchestration, Edge-to-Cloud-as-a-Service(E2CaaS).
- We are going to discuss how “software service development” and “advance ML and AI techniques” can mix in the smart cities to provide facilities for citizens’ demands, such as “intelligent resource management techniques for the service execution.” In addition, we also care about the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), data privacy, and the security concerns of citizens in our ICT architecture design.
To sum up, we are looking to design an integral ICT architectural solution for “ML&AI-E2C: ML&AI at Edge-to-Cloud orchestration.” One of the facilities of “ML&AI-E2C” solutions can be realized in the “intelligent resource management for the service execution” at the middleware platform of large-scale IoT networks of smart cities.
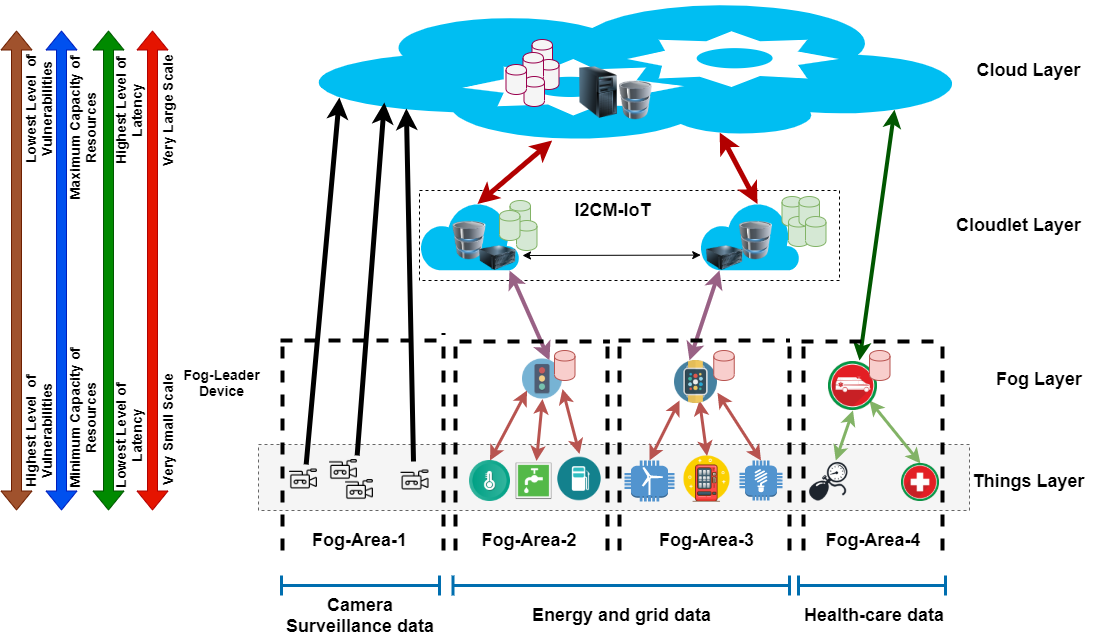
Figure 2. Our proposed hybrid ICT architecture in the smart city based on different city-data-source formats [2] and some relevant information about the main “large-scale ICT architecture” idea available here
3. Challenges (The main reference of this part is here):
Why is it necessary to consider and extend “Cloud Services” and “ML and AI techniques” at the edge of IoT networks?
- Data Growth in terms of “Size,” “Time,” and “Scale” (Large-Scale ICT and its Data Management): Exponential growth of city-data in widely distributed storage media of Smart Cities, as data is the main ingredient for ML and AI techniques and algorithms;
- Data Privacy: Citizens and data stakeholders may not be willing to share their information in a public data storage (e.g., Cloud technologies platform);
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR is a regulation in the EU law on data protection and privacy. GDPR also addresses the transfer of personal data outside the EU and EEA areas;
- Cybersecurity Concerns: In case of an attack at the centralized platform place (Cloud technologies) or multi-attacks at the IoT devices network will occur, how can we collect and send data/datasets to a centralized platform place to extract our knowledge requirements through data analysis/analytic and ML and AI techniques?
- Complexities of running and managing complex ML and AI techniques at the edge of networks: Due to computational and memory limitations of IoT devices and low processing abilities at the edge of the Smart City networks, IoT devices are often not capable of running and managing complex ML and AI techniques and algorithms at the edge of the Smart City networks.
- Cost of Cloud services: In most cases, having Cloud storage and services can be quite expensive. Being charged year after year for a monthly or annual subscription can add up. Cloud storage and services providers know that customers will pay those high fees to have their data backed up and ultimately to have peace of mind.
4. Introduction:
A large-scale number of heterogeneous internet of things (IoT) devices engage in any smart city’s IoT networks. To organize and provide effective integration between all IoT data sources in smart city IoT networks, decentralized-to-centralized information communication technology (DC2C-ICT) and distributed-to-centralized ICT (D2C-ICT) architectures have been designed as a collaborative, coordinated, and hierarchical edge-to-cloud computing orchestration platform. Our recent studies present how our proposed ICT architectures may map to requirements of large-scale IoT networks of smart cities and provide facilities for managing data, resources, software services, and cybersecurity and network [3].
Developing software services in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities is a quite challenging job in different multilevel ICT architecture, as shown in Fig. 3. It is also required to execute some “software services execution tasks.” Usually, each task has diverse necessities, which have to be fulfilled. One of the main “software service execution tasks” is related to large-scale ICT “resource management.” Recently, there are several efforts to design the intelligent mechanism for “software service execution tasks” and their related “resource management” mechanism in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities. However, there are still infant design stage and more technical decision and research required. One of the great intelligent design solutions proposes through edge-to-cloud computing platform orchestration and integration to the usage of advanced machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to create an intelligent system for “software service execution” tasks and their “resource management” mechanism.
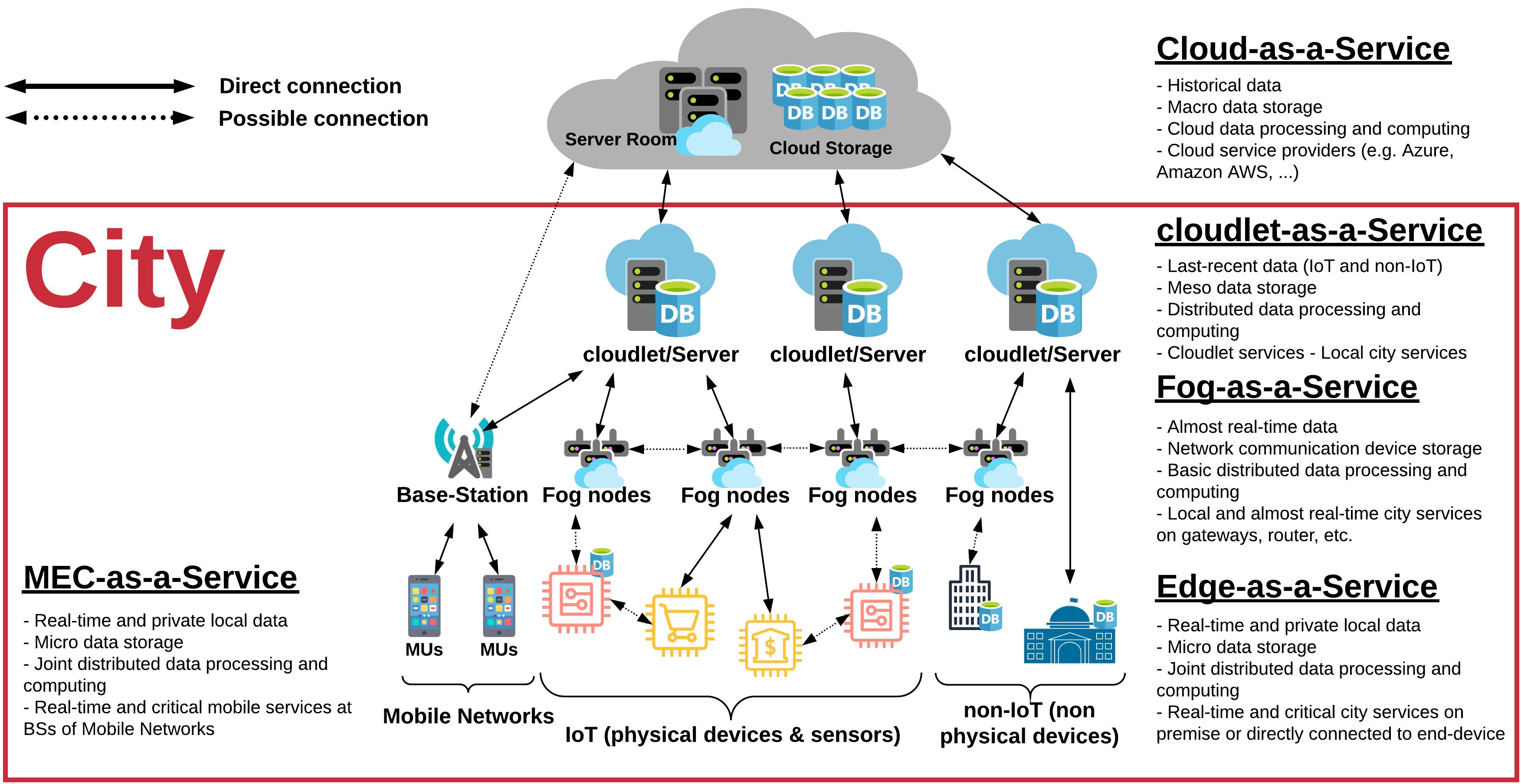
Figure 3. Different Software Service layers from edge-to-cloud orchestration [4]
“Resource statistical information” presents a significant role in efficiently implementing the “resource management” mechanism for the consumers’ software services execution platform in smart cities. On the one hand, continuous monitoring of engaging devices can produce many “resource statistical information” through large-scale IoT networks of smart cities. On the other hand, with this statistical information’s help, it is getting much simpler to realize the device’s availability and suitability for executing some software services tasks for building software services in smart cities. Accordingly, to ensure more reliable software service facilities for any latency-sensitive software services requirements in the smart cities, designing an intelligent ICT architecture and their computing platform eco-system is quite challenging and necessary. This ICT architecture may make it possible to organize securely distribute the city-data and resource statistical information over smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks.
Designing an advanced and more intelligent ICT eco-system is required to consider effective mechanism management to utilize IoT resources in smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks. Notably, effective utilization of resources guarantees decreasing unnecessary resource consumption and develops the overall ICT eco-system performance. Generally, the utilization and resource handling process are essentially related to the “resource selection and allocation mechanism” strategies. However, on-demand “resource selection and allocation” is a complex task for any large-scale D2C-ICT architecture eco-system. Also, the prediction of ICT resource usage (such as network communication bandwidth, CPU, hard disk, and ram) and their related performance (e.g., task execution time) can help identify their appropriateness executing some tasks for building software services in smart cities. Therefore, adopting the advanced ML and AI techniques can be valuable for designing an advanced and modern resource allocation mechanism in smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks. However, adopting and implementing advanced ML and AI techniques in a large-scale ICT architecture eco-system in smart cities can be quite complex and in an infant design and development stage among researchers in academia and industries. The overall diversification and many other issues can especially pose a massive challenge for successfully executing the advanced ML and AI techniques to predict the software services requirements in smart cities’ large-scale IoT networks.
In the case of the combined and hierarchical computing platform and ICT architecture (i.e., Fog-to-Cloud or Fog-to-cloudlet-to-Cloud) from the distributed-to-centralized schema, it is essential to define the architectural framework for predicting the “resource management” requirements based on various ML and AI techniques. This framework makes numerous facilities to analyze varieties of “Resource statistical information” datasets from various IoT devices in large-scale IoT networks of smart cities. Therefore, it is essential to define and design that kind of architectural framework for combined Edge to Cloud technologies systems to manage and predict resource management’ requirements, demanding a specific effort from the research community. Currently, “federated learning” and “replicated learning” techniques provide attractive facilities where can be applied through different architectural layers of Edge-to-Cloud orchestration to train varieties of resource statistical datasets as well as using different ML and AI techniques. One example of the combination of DC2C-ICT architecture and advanced FL models is shown in Fig. 4.
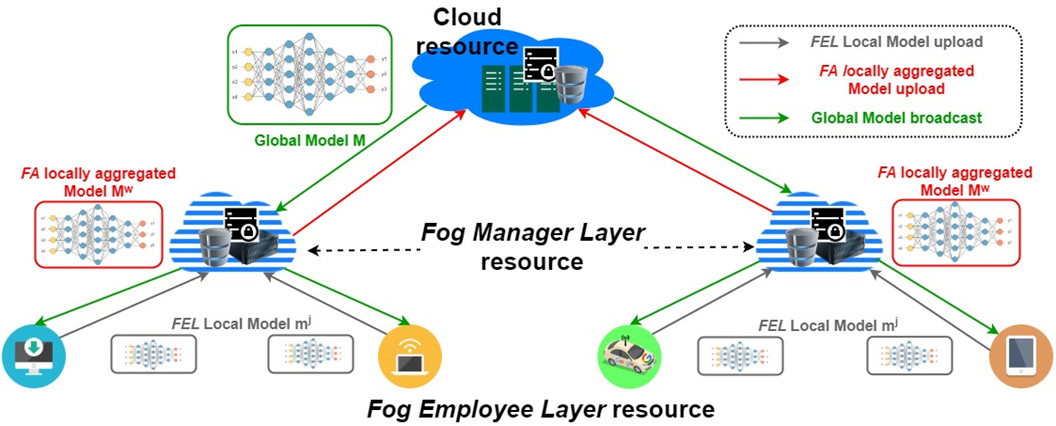
Figure 4. Federated Learning for prediction of “resource management” through DC2C-ICT architecture [5]
References:
[1] Figure extracted from “https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-iaas/.”
[2] A. Sinaeepourfard, et al., “ICT architectures for large-scale IoT networks of smart cities,” preparing for the journal submission – please follow the new update regularly.
[3] A. Sinaeepourfard, J. Krogstie, S. Sengupta, “Distributed-to-Centralized Data Management: A New Sense of Large-Scale ICT Management of Smart City IoT Networks,” IEEE Internet of Things Magazine (IEEE IoTM), 2020.
[4] J. Robberechts, A. Sinaeepourfard, T. Goethals, and B. Volckaert, “A Novel Edge-to-Cloud-as-a-Service (E2CaaS) Model for Building Software Services in Smart Cities,” IEEE Int’l. Conf. Mobile Data Management (MDM), 2020.
[5] S. Sengupta, J. Garcia, X. Masip-Bruin, “Collaborative learning-based Schema for Predicting Resource Usage and Performance in F2C Paradigm,” IEEE International Conference on Advanced Networks and Telecommunications Systems (IEEE ANTS), 2020
Organization
Organizing Committee
Workshop Organizer and Idea Creator

Ask him about “Data/Software Service Management applied in IoT/Edge-to-Cloud Computing orchestration/Smart Cities,” and “Large-Scale ICT/IoT networks management of Smart Cities”
Amir Sinaeepourfard, Ph.D., is a “research associate” and a “Postdoctoral candidate” at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway. He received a Ph.D. in Computer Architecture (focused on data and software management) with First Class Honors (Excellent CumLaude) from Technical University of Catalonia (UPC) in Spain, in 2018. He was a fellow of the FI-DGR fellowship program of the Generalitat de Catalunya in Spain during his Ph.D. studies. Based on his Ph.D. studies, he proposed several novel contributions for Large-Scale ICT management in smart cities through Edge-to-Cloud orchestration, e.g., “D2C-DM: Distributed-to-Centralized Data Management,” and “E2CaaS: Edge-to-Cloud-as-a-Service Model for Building Software Services.” One of his publications, based on his Ph.D. thesis, received the IFIP Med-Hoc-Net paper of the “best paper year award” for 2016. He has significant hands-on experiences in both academic research and organizing scientific events/seminars/workshops/conferences in his field. He is the “Workshop Organizer and Idea Creator” of a series of “3SCity-E2C: Building Software Services in Smart City through Edge-to-Cloud Orchestration international workshops,” including “3SCity-E2C” and “D2C-ML&AI / Special D2C-ML&AI Conference Track,” “Intelligent Resource Management Mechanism for Service Execution of Large-Scale IoT Networks,” and “The ICT in Smart City Day event (ICT-SCity).” His Google Scholar citation as of March 2021 was 229, and his H-index was 10. He has been quite well-experienced in leadership activities in academia and industries (such as the “e-banking manager,” “technical supervisor/leader of master and bachelor students”). He is an active member of several European projects and consortiums for technical collaboration/responsibilities of several tasks, reports, deliverables, and publications (such as “H2020 mF2C: Towards an Open, Secure, Decentralized and Coordinated Fog-to-Cloud Management Ecosystem“), the Research Council of Norway (such as ZEN: Zero Emission Neighbourhood), and the Spanish Government Grant (such as FI-DGR fellowship program of the Generalitat de Catalunya).
His current research interest includes “Smart Cities, “IoT,” “Large-Scale IoT Management,” “Big Data Management,” “Cloud/Fog/Edge Computing,” “Data and Software Management (including Centralized and Distributed).”
His publication lists> Google Scholar
“Workshop Committee Member” & “Intellectual Technical Contribution to the Idea Creator”

Ask him about “ML applied in IoT” and “Resource Management in Fog/Edge Computing”
Souvik Sengupta, Ph.D., is a former researcher at CRAAX lab, UPC, Spain, and he is currently working at Fundació i2CAT, Spain, as a research engineer. He is working in the area of resource management strategy in fog-to-cloud computing using machine learning strategies. He has a fellowship from FPI, which is provided by the Ministry of Science and Innovation, Spain. In the past, he was awarded by the Erasmus Mundus Scholarship, which the European Commission has provided for the “c-LINK-centre of excellence for Learning, Innovation, Networking and Knowledge,” Erasmus Mundus Action 2 project (372242-1-2012-1-UK-ERA MUNDUS-EMA21). One of his publications received the “International Conference on Smart Communications in Network Technologies (SaCoNeT)” paper of the year award for 2018.
His current research interest includes “Fog/Edge computing,” “Cloud Computing,” “IoT,” “Resource Management,” “Database Management,” and “Machine Learning applied in IoT”
His publication lists> orchid
Workshop Committee Members

Ask her about “Resource and Service Management in Fog/Edge Computing” and “Smart Cities”
Shehenaz Shaik, Ph.D., holds Ph.D. in Computer Science from Auburn University, AL, USA. She holds M.S. in Computer Science from University of North Texas, TX, USA as well as B.Tech. in Computer Science and Engineering from Sri Krishna Devaraya University, AP, India. She has worked with Tata Consultancy Services Ltd., India, the largest IT company of India, for more than a decade and contributed to the design and development of Physical and Virtual Infrastructure Solutions. She held several roles as Infrastructure Solutions Engineer, Cloud Solutions Architect, Enterprise Storage Technical Presales Architect, etc. Her doctoral dissertation topic is, “Resource and Service Management in Fog Computing.” She has also developed a simulator, PFogSim, to simulate large-scale Fog Computing environments with thousands of fog nodes, data-generating devices, and data consuming users, which are possibly mobile during the simulation. She has researched and published several papers on fog computing at various conferences.
Her current research interest includes “Fog/Edge/Cloud Computing,” “Smart Cities,” “Data management,” “Data Mining,” “Internet of Things,” “Storage Networks,” and “Hyper Converged Infrastructure.”
Her publication lists> Google Scholar

Ask him about “Software Engineering” and “IoT Security and Privacy”
Phu H. Nguyen, Ph.D., is a Research Scientist at SINTEF, as a member of the Secure IoT Software group with a focus on tools and methodologies for software development and operation of heterogeneous and autonomous, yet secure and privacy-aware systems spanning across the Cloud, the Edge, and the IoT. He has experience working on international research projects as well as research and development projects with industry in Norway. He has a very international education and research background, from Vietnam (BSc) to the Netherlands (MSc), Luxembourg (Ph.D.), and Norway. He is also an active reviewer and organiser of high-impact journals (e.g., TSE, SoSyM, INFSOF, JSS), conferences, and workshops. He was awarded a certificate for exceptional contributions, support, and commitment in the organization of the Sixth IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST 2013), IBM award for displaying exceptional personal dedication, teamwork, and contribution to the ibm.com project 2007, and the first prize at the LuxDoc Science Slam 2014 for communicating research to the public.
His current research interest includes “IoT,” “Microservices Architecture,” “Cloud to Fog/Edge,” “C-ITS,” and “IoT Security and Privacy.”
Her publication lists> Google Scholar

Ask him about “Resource Allocation and Management” and “Fog computing”
Vitor Barbosa Souza, Ph.D., is a Professor at the Federal University of Viçosa (UFV) in Brazil. He has Bachelor’s Degree (2006) and a Master’s Degree (2010) in Computer Science at UFV and a Ph.D. (Cum Laude) in Computer Architecture at the Technical University of Catalonia (UPC) in Spain (2018) with a focus on advanced network architectures. His doctoral thesis «Mechanisms for service-oriented resource allocation in IoT» has been the most downloaded among those published in the years 2017-2018 / 2018-2019 and published at the institutional UPC repository. He has been a member of European projects such as H2020 mF2C and H2020 GUAU. Also, he is an active reviewer of relevant journals such as ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), International Journal of Communication Systems (IJCS), Computer Communications, and Internet of Things Journal. Recent work is related to the provisioning of Control-as-a-Service in highly dynamic and heterogeneous fog environments and the employment of machine learning techniques for enhanced QoS in collaborative service-oriented architectures.
His current research interest includes “Fog computing,” “Cloud computing,” “IoT,” “QoS,” “5G,” and “Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)”

Ask him about “Fog/Edge Computing” and “Cybersecurity & Privacy”
Antonio Salis, is R&D Project manager in Engineering Sardegna. Since 1988 he has been working in software and integration projects, where he played several roles, from developer to system architect and technical lead, with TECHSO (IBM participated), ST Microelectronics, Video On Line, Telecom Italia, and Tiscali, where acted as Corporate Project Manager and responsible for Quality, Information Security and Data Privacy Compliance. Previously involved in EU FP7 Projects, he is currently involved in several EU H2020 projects in ICT, SPIRE, and COVID calls, and supports some international workshops, including “3SCity-E2C” and “D2C-ML&AI”. He received a master’s degree in computer science from the University of Pisa.
His current research interest includes “Cloud,” “Fog/Edge computing,” “IoT and Big Data,” “ML/AI and Cognitive Computing,” and “Cybersecurity & Privacy in ICT and Industrial sectors.”
His publication lists> https://dblp.uni-trier.de/pers/hd/s/Salis:Antonio
Scientific Committee
- Pierluigi Salvo Rossi, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway
- Mamoun Alazab, College of Engineering, IT and Environment, Australia
- Antonio J. Jara, University of Applied Sciences Western, Switzerland
- Alireza Jolfaei, Macquarie University, Australia
- Vinayakumar Ravi, University of Cincinnati, USA
- Dirk Ahlers, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway
- Amirhosein Taherkordi, Universitetet i Oslo (UiO), Norway
- Jens Jensen, UK Research and Innovation-Science and Technology Facilities Council (UKRI-STFC), UK
- Shuaib Siddiqui, i2CAT Foundation, Spain
- Deepak Puthal, Newcastle University, UK
- Mohamed Hamdy, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway
- Alexander Norta, TalTech, Estonia
- Octavio Loyola-González, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Mexico
- Suman Sankar Bhunia, PwC Inc., India
- Saad Qaisar, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan
- Ali Dorri, Queensland University of Technology (QUT), Australia
- Gowri Sankar Ramachandran, University of Southern California, USA
- Sarang Kahvazadeh, Centre Tecnològic de Telecomunicacions de Catalunya (CTTC), Spain
- Qaisar Shafi, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan
Keynote speakers
TBA
Partners
NTNU – Norwegian University of Science and Technology

NTNU is a university with an international focus, with headquarters in Trondheim and campuses in Ålesund and Gjøvik.
NTNU has a main profile in science and technology, a variety of programs of professional study, and great academic breadth that also includes the humanities, social sciences, economics, medicine, health sciences, educational science, architecture, entrepreneurship, art disciplines, and artistic activities.
ZEN – Zero Emission Neighbourhoods in Smart Cities

The ZEN Research Centre conducts research on Zero-Emission Neighbourhoods (ZEN) in smart cities.
The main goal is to develop solutions for future buildings and neighbourhoods with no greenhouse gas emissions and thereby contribute to a low carbon society.
Submission
Topics
The workshop provides a forum to discuss the theoretical foundations and original technical contributions of developing Software Services through Large-Scale data management architecture and their related ML/AI techniques in smart cities based on edge-to-cloud computing solutions, by bringing together industry, academia, engineers, and researchers. Also, this series of our workshops aim to integrate all idea of the past “3SCity-E2C” workshop, including “3SCity-E2C,” “D2C-ML&AI,” “Special Track of D2C-ML&AI”. So, we propose the idea of how we can build the “intelligent resource management mechanism for Service Execution of large-scale IoT Networks.” This highlights the collaboration of “Software Engineering Development,” “ML/AI applied to IoT,” “facilities of multilevel ICT architectures,” and “edge-to-cloud computing orchestration.” We invite submissions of the unpublished work on the following topics (but not limited to):
- Software Service Management Technologies, Architecture, and Platforms through Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in Smart Cities;
- Serverless Architecture for large-scale IoT networks of smart cities;
- Microservice Architecture for large-scale IoT networks of smart cities;
- Data Management Technologies, Architecture, and Platforms through Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in Smart Cities;
- Resource Management Technologies, Architecture, and Platforms through Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in Smart Cities;
- ICT Technologies, Architecture, and Platforms through Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in Smart Cities;
- Federated Learning/Replicated Learning through large-scale IoT networks of smart cities;
- Advance ML and AI techniques for multilevel ICT architecture in smart cities;
- Innovative software services in Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in smart cities, particularly IoT, smart sensing, and Artificial Intelligence technology;
- Quality of Edge-to-Cloud software services in smart cities;
- Edge-based or Edge-to-Cloud based real-time applications in smart cities;
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) for Edge computing and Edge-to-Cloud computing networks in smart cities;
- Load balancing and service selection at the Edge computing networks in smart cities;
Important dates
- Opening of Workshop Papers for Acceptance: March 1, 2021
- Deadline for Workshop Papers: April 1, 2021
- Decision on Acceptance/Rejection of the Workshop Papers: April 10, 2021
- Camera-ready Deadline: April 24, 2021 (Firm deadline)
Submission instruction
3SCity-E2C proceedings will be published in the combined 22nd IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM) 2021 proceedings and will be submitted to IEEE Xplore® digital library. The following paper categories are welcome:
- All papers must be original and not simultaneously submitted to another journal or conference;
- All papers need to be submitted electronically in PDF format through EasyChair (TBA);
- Papers must be formatted for the 8.5×11-inch paper;
- The length of the paper must be no more than 6 pages in the IEEE double-column format (10-pt font), including references and everything;
- The paper format must follow the IEEE template, https://www.ieee.org/conferences/publishing/templates.html;
- Papers should neither have been published elsewhere nor being currently under review by another conference or journal;
- The reviews will be single-blind;
- Each submitted paper will review by three reviewers, including TPC and Committee members;
- At least one of the authors of every accepted paper must register and present the paper at the workshop;
- Camera-ready instruction is available on http://mdmconferences.org/mdm2021/cfp.html;
- Registration instruction is available on TBA.
Program
TBA
Venue
Please visit this link for further information.
Contact
For further information, please contact us at a.sinaee@ntnu.no. Please put the title of your email “3SCity-E2C 2021 Workshop-Question”.




